RIA
Root Image Analysis in ImageJ
Simple root image analysis in ImageJ
Requirements
Images need to be in black and white, with the roots in black, for a good analysis. If analysing shoot, please rotate the image such as the shoot is upside-down.
Installation
- Install FIJI
- Download the file
RIA_J.jarfrom HERE - Launch FIJI and go to
Plug-in > Install Plugin - Select the
RIA_J.jarfile - Relaunch FIJI
You’re done!
Using the plugin
- Lunch FIJI
- Go to
Plug-ins > RIA - A new window will open. Go to the
RIAJ Analysistab - Choose the folder containing your images. You can either copy/paste it in the field, or navigate with the
Choose folderbutton. Be careful that the path is correct. - Tick the desired options:
Save images: will save an images illustrating the different analysis (such as the convexhull, shape, …). This take more time and more space.Even the tips: Save an image with the tips detection. Takes even more time (more than double, for some obscur reason to me).Verbatim: print in the log windown the current step perfomed in the analysisSave TPS: Save a TPS file, that could be then used for a morphometric analysis.
- Set the scale
- Set the minimal root size, in pixels
- Choose the export path for the results (as a
csvfile) - Click the
Run analysisbutton
Screencast of RIA-J
Measurements
- diam_max: max diameter
- diam_mean: mean diameter
- diam_mode: most frequent diameter (mode)
- length: length of the skeleton of the root system
- area: projected area of the root system
- width: The maximal width of the root system
- depth: The maximal depth of the root system
- width_depth_ratio: ratio between the width and the depth of the root system
- com_x: relative coordinate of the center of mass of the root system (x)
- com_y: relative coordinate of the center of mass of the root system (y)
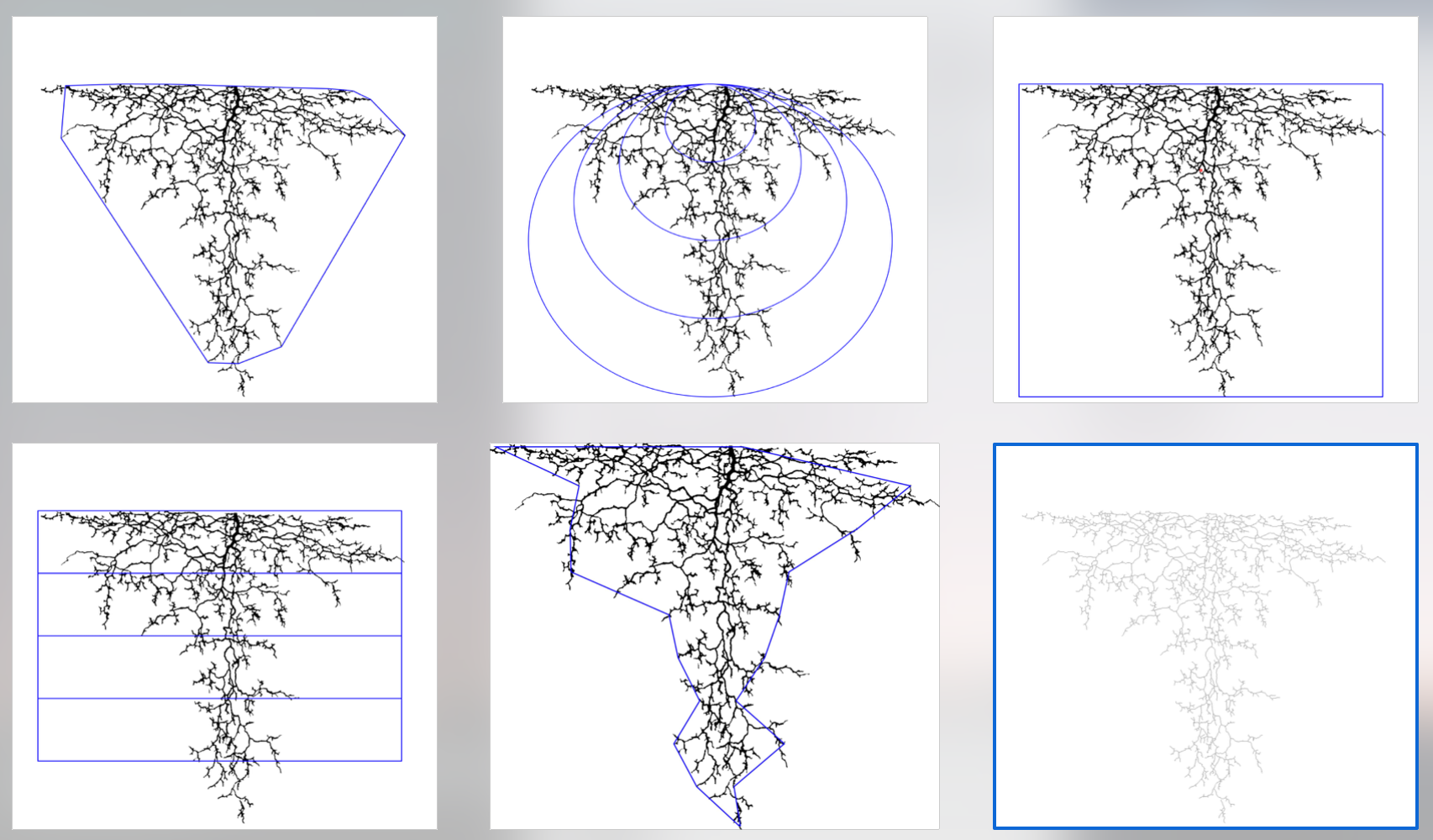
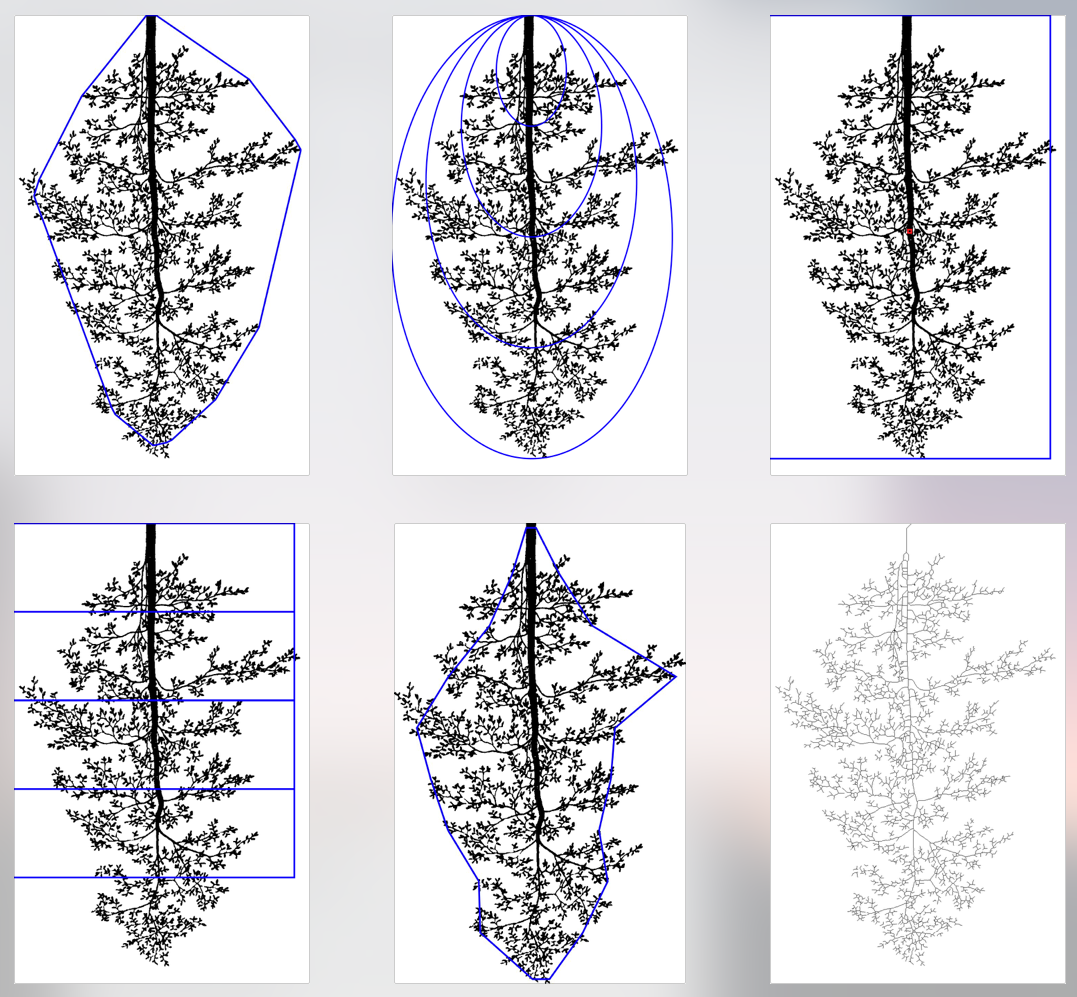
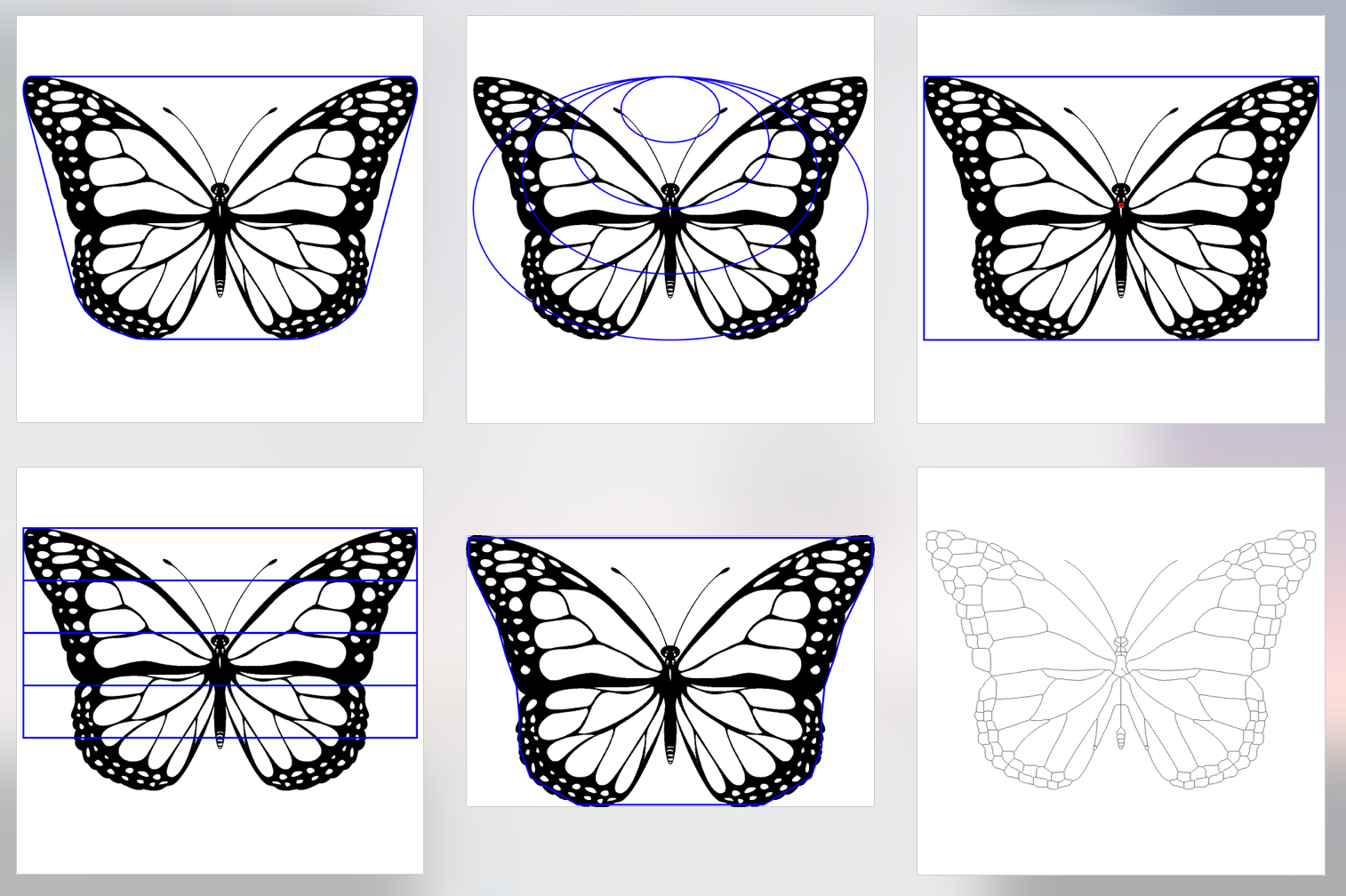
- ellips_##: Proportion of root area in ellipses of different size, centered on the top of the root system (see figure below for graphical explanation)
- rect_##: Proportion of root area in 4 layers of the root system (see figure below for graphical explanation)
- directionality: Mean direction of the root segments in the root system
- tip_count: number of end branches in the root system skeleton
- convexhull: Area of the smallest convex shape encapsulating the root system
Cross-hori and Cross-vert For these, we scan the root system skeleton with a horizontal/vertical line. During the scan, at each y/x position, we count the number of roots crossing the line. We then compute either the maximal or mean number of roots crossed during the scanning. For the horizontal scanning, we divided the root system in 30 layers. So cross-hori-mean-# can be seen as a root number profile along the depth of the root system.
- cross-hori-#-mean : Mean root detected when scanning the root system with a horizontal line at the depth #
- cross-hori-#-max : Max root detected when scanning the root system with a horizontal line at the depth #
- cross-vert-mean: Mean number of root detected when scanning the root system with a vertical line
- cross-vert-max: Max number of root detected when scanning the root system with a vertical line
Coord / Diff / Cumul We dived the root system in ten equal layers. In each layer, we find the min and max x values of the root segments. With this, we can compute a shape of the root system, with only 10 pairs of x values.
- coord_x# : x coordinates of the shape of the root system.
- diff_x# : difference between x values for each layer of the shape. Desctibe the width of the root system in each layer
- cumul_x# : cumulative width of the different layers of the root system
Example of visual output
Root
Shoot
Butterfly
Cite us
If you use RIA-J please use the following citation:
Lobet G, Koevoets IT, Noll M, Tocquin P, Meyer PE, Pagès L, et al. Using a structural root system model to evaluate and improve the accuracy of root image analysis pipelines. Front Plant Sci. Frontiers; 2017;8. doi:10.3389/fpls.2017.00447